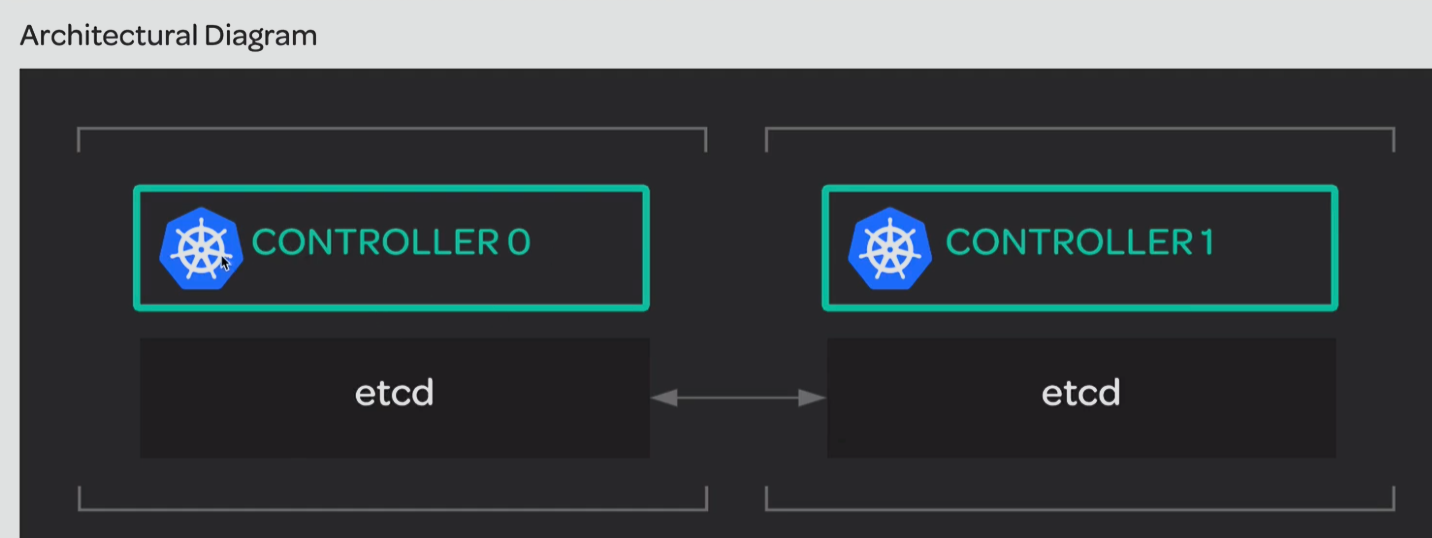
Your team is working on setting up a new Kubernetes cluster. Because etcd is one of the necessary components of Kubernetes, the team needs an etcd cluster configured to run across all the servers that will become the Kubernetes control nodes. You have been given the task of setting up an etcd cluster that will be used to support Kubernetes.
What we will learn:
- Install the etcd binary on both control nodes.
- Configure and start the
etcdservice on both control nodes.
Installing the etcd binary on both controller nodes
wget -q --show-progress --https-only --timestamping \
"https://github.com/coreos/etcd/releases/download/v3.3.5/etcd-v3.3.5-linux-amd64.tar.gz"
tar -xvf etcd-v3.3.5-linux-amd64.tar.gz
sudo mv etcd-v3.3.5-linux-amd64/etcd* /usr/local/bin/This set of commands is used to download, extract, and install etcd version 3.3.5 on a Linux system.
sudo mkdir -p /etc/etcd /var/lib/etcd
sudo cp ca.pem kubernetes-key.pem kubernetes.pem /etc/etcd/Configure and start the etcd service on both control nodes.
Now we will designate names for these controllers:
ETCD_NAME=controller-0Execute this in controller 0 to set this variable
ETCD_NAME=controller-1Execute this in controller 1 to set this variable
Let's now set the internal IP Variables, these can be done by curling the Amazon Web Services API which will automatically assign this for you.
INTERNAL_IP=$(curl http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/local-ipv4)Now we will set variables CONTROLLER_0_INTERNAL_IP= and CONTROLLER_1_INTERNAL_IP= the values for these can be obtained through the LAB settings provided, we will have to set these variables for each machine/worker node.

Now we will create a standard systemd unit file
cat << EOF | sudo tee /etc/systemd/system/etcd.service
[Unit]
Description=etcd
Documentation=https://github.com/coreos
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/etcd \\
--name ${ETCD_NAME} \\
--cert-file=/etc/etcd/kubernetes.pem \\
--key-file=/etc/etcd/kubernetes-key.pem \\
--peer-cert-file=/etc/etcd/kubernetes.pem \\
--peer-key-file=/etc/etcd/kubernetes-key.pem \\
--trusted-ca-file=/etc/etcd/ca.pem \\
--peer-trusted-ca-file=/etc/etcd/ca.pem \\
--peer-client-cert-auth \\
--client-cert-auth \\
--initial-advertise-peer-urls https://${INTERNAL_IP}:2380 \\
--listen-peer-urls https://${INTERNAL_IP}:2380 \\
--listen-client-urls https://${INTERNAL_IP}:2379,https://127.0.0.1:2379 \\
--advertise-client-urls https://${INTERNAL_IP}:2379 \\
--initial-cluster-token etcd-cluster-0 \\
--initial-cluster controller-0=https://${CONTROLLER_0_INTERNAL_IP}:2380,controller-1=https://${CONTROLLER_1_INTERNAL_IP}:2380 \\
--initial-cluster-state new \\
--data-dir=/var/lib/etcd
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=5
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOFNow we will start the etcd service
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable etcd
sudo systemctl start etcdWe need to do a daemon reload after big changes and enable startup.
So how do we verify this is set up correctly?
sudo ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl member list \
--endpoints=https://127.0.0.1:2379 \
--cacert=/etc/etcd/ca.pem \
--cert=/etc/etcd/kubernetes.pem \
--key=/etc/etcd/kubernetes-key.pemThis command securely connects to the local etcd instance using client certificates and retrieves a list of the nodes (members) in the etcd cluster via the v3 API.
We should see a list of controller 0 and controller 1 with their respective IPS and configurations & both nodes showing up.
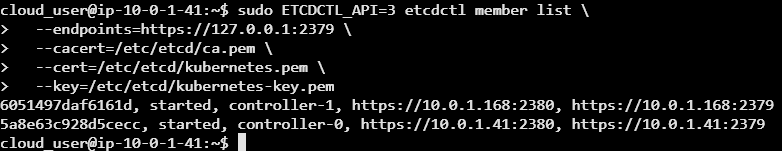
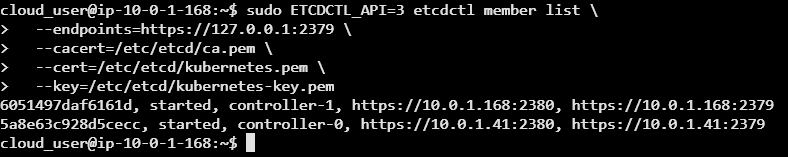
This activity is focused on setting up an etcd cluster to support a new Kubernetes cluster across two control nodes. It involves installing the etcd binaries on both nodes, configuring security certificates, and setting up intercommunication between the nodes.
The process includes creating necessary directories, setting node names, configuring IP addresses, and writing a systemd service file to manage the etcd service. After starting the etcd service, verification is performed by listing the cluster members to ensure both nodes are properly configured and can communicate with each other.